One in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime, making skin cancer the most common form of cancer in the United States.
What are the most common types of skin cancer?
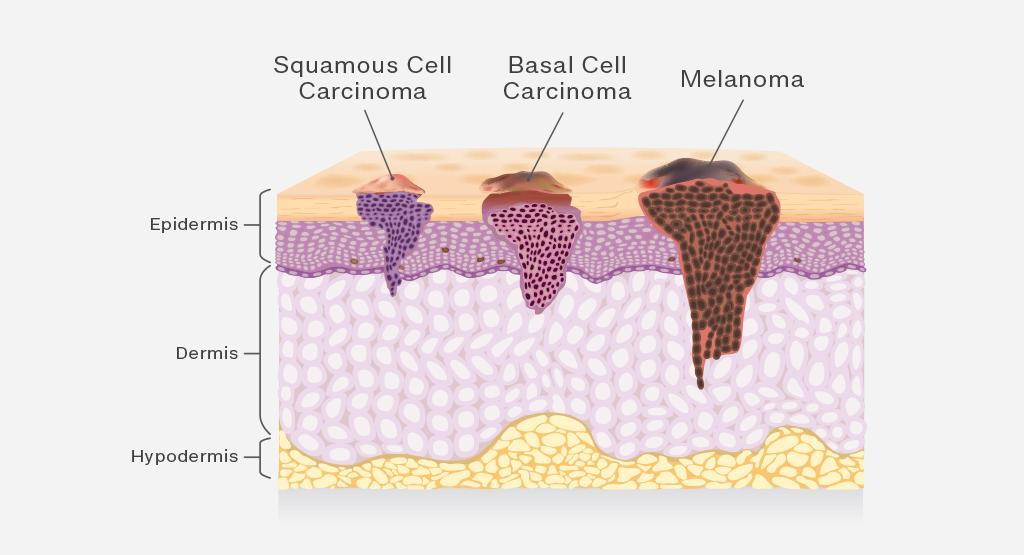
The three most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are highly treatable if detected early and treated properly. Basal and Squamous cell are found in areas that receive sun exposure. Basal and squamous cell skin cancers can present on the skin as a slowly growing, non-healing spot that sometimes bleeds, red scaling or crusting patch, or a pimple that does not heal.
Melanoma may appear on the skin suddenly as new moles but can also develop within an existing mole. Melanoma is highly treatable when detected early, but advanced melanoma can spread to the lymph nodes and internal organs, which can result in death.
The five-year survival rate for people whose melanoma is detected and treated before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%. Having five or more sunburns doubles your risk for melanoma. Melanoma often presents as an irregular new or changing existing mole.
How can I reduce risk of skin cancer?
It is important to protect your skin from the sun’s damaging ultraviolet rays to reduce your risk of skin cancer. Avoid the sun between 10 am and 2 pm and wear sun protective clothing. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and reapply every two hours. Most adults need about one ounce, enough to fill a shot glass, to fully cover their body.
Annual skin exams can help detect skin cancer at its earliest and most treatable stages. These exams can also allow your dermatologist to find and remove precancerous lesions before they develop into skin cancer.
If you notice a mole on your skin, you should follow the ABCDE rule, which outlines the warning signs of melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border irregularity: The edges are ragged, notched or blurred.
- Color: The pigmentation is not uniform. Different shades of tan, brown or black are often present. Dashes of red, white, and blue can add to the mottled appearance.
- Diameter: While melanomas are usually greater than 6mm in diameter when diagnosed, they can be smaller.
- Evolving: The mole or skin lesion looks different from the rest or is changing in size, shape or color.



